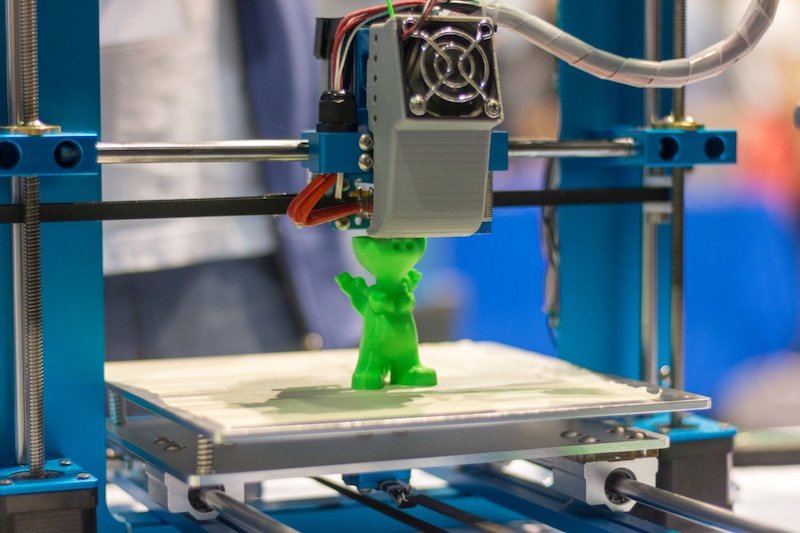
Understanding the requirements for both prototyping and rapid prototyping are essential for a number of reasons, especially for professionals working in tech development, engineering, manufacturing, and product layout.
Table of Contents
- 1 Here are some reasons why someone working in particular sectors would need to know everything about this:
- 2 What are Prototyping and Rapid Prototyping?
- 3 Advantages of Prototyping and speedy Prototyping:
- 4 Associated questions and answers:
- 4.1 How does rapid Prototyping contribute to sustainable product design and development?
- 4.2 In what methods can fast Prototyping be integrated into educational curriculums to enhance knowledge of engineering and layout?
- 4.3 How has fast Prototyping motivated the custom production of scientific devices and implants?
- 4.4 What function does fast prototyping play in the improvement of wearable tech?
- 4.5 How might technologies like AI and device learning enhance speedy prototyping techniques?
- 4.6 What effect might advances in product technology have on the future of rapid Prototyping?
- 5 Conclusion:
Here are some reasons why someone working in particular sectors would need to know everything about this:
Innovation Acceleration
One important factor in accelerating innovation is the rapid prototype and low volume manufacturing process. It makes it possible to quickly explore and improve ideas, which is crucial in a market that moves fast and fiercely. Whilst a brand new concept is evolving, a prototype provides the primary tangible illustration of the idea, enabling designers and engineers to discover its feasibility, capability, and ability in a real-world manner. This hands-on approach can cause unexpected discoveries and enhancements, fostering a culture of continuous innovation. Speedy Prototyping, to be exact, significantly hastens this system because it enables a multitude of iterations to be created and examined in a fraction of the time it would take with traditional methods. This fast iteration cycle allows thoughts to be advanced and fleshed out at a pace that stays on track or even sets market trends.
Risk Mitigation
Prototyping performs a vital position in reducing the risks associated with new product improvement. When constructing a prototype, capability troubles within the design, substances, ergonomics, capability, and manufacturability can be identified and addressed early in the development process. This early detection is critical as it prevents highly-priced mistakes that are only caught after a product goes into mass manufacturing. It also permits the trying out and validation of assumptions made at some stage in the layout segment, ensuring that the very last product will operate as intended. Addressing these problems for the duration of the prototyping phase is generally a great deal, much less highly priced and time-consuming than making modifications after rapid manufacturing has started.
Stakeholder conversation
Prototypes are priceless pieces of equipment for speaking with stakeholders. They provide a bodily illustration of an idea or concept that is way better than drawings or digital variations. For investors, a prototype can demonstrate the feasibility of a product and its marketplace ability. For clients, it can help them visualize the final product and offer feedback. For group members, it serves as a concrete reference point that can direct and align efforts. This tangible form of verbal exchange can be very crucial for securing investment, gaining consumer approval, or making sure that a product meets the market’s or a customer’s precise wishes.
User-Centered Design
Prototyping is vital for implementing an approach that is user-centered and design-oriented. It enables engineers and designers to test their products on real people, receiving invaluable input on customer preferences, ergonomics, and usability. The layout may then be improved and modified based on this feedback, ensuring that the finished result not only serves a function but also satisfies user expectations. Testing by users all through the prototyping period can uncover insights that might not be obvious through design and simulation solely, leading to merchandise that can be more likely to prevail inside the marketplace.
Cost and time efficiency
Fast Prototyping makes for an extra price-reducing and time-conserving mechanism for product improvement compared to standard manufacturing strategies. Conventional Prototyping may be time-consuming and highly-priced, especially if it involves complicated tooling or production approaches. Speedy prototyping technologies like 3D printing, CNC machining, and laser reducing, then again, allow for prototypes to be produced much faster and frequently at a lower fee. This speed and efficiency allow extra iterations and refinements in an identical timeframe and budget, leading to a superior final product without appreciably growing development costs. This performance is specifically useful in industries in which time to market is essential.
What are Prototyping and Rapid Prototyping?
Prototyping is the manner of creating an initial model or sample of a product to check and validate the design idea. It is a sensible approach to test with design ideas, capability, and value. Conventional Prototyping can contain homemade fashions or easier representations of the very last product.
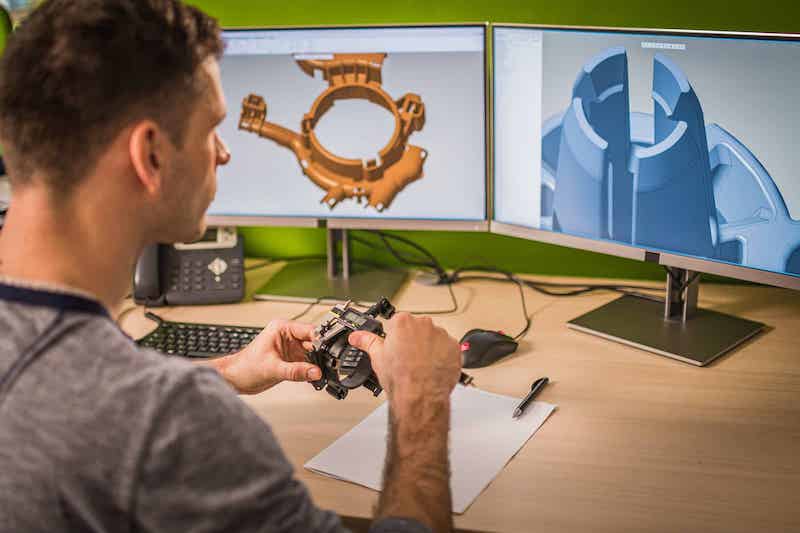

Fast Prototyping refers to techniques that allow for the rapid fabrication of a scale version of a part or assembly, making use of 3D CAD info. It encompasses diverse technology, most notably 3-D printing, but also with CNC machining, laser cutting, and speedy injection moulding. The important thing here is pace and performance, permitting designers and engineers to iterate designs quickly.
Advantages of Prototyping and speedy Prototyping:
Pace: Speedy Prototyping appreciably reduces the time from concept to physical model.
Flexibility: It makes for smooth adjustments and iterations of a layout.
Value-Effectiveness: Reduces the overall development costs by identifying troubles early.
Enhanced Creativity: Encourages experimental strategies and solutions that are innovative.
Enhanced Accuracy: Provides high fidelity to the final product, ensuring the prototype is a true representation.
Useful trying out: allows for testing the capability and overall performance of a layout.
Marketplace feedback: facilitates early checking out with actual customers or market research.
Complexity managing: Can create complicated designs that aren’t possible with traditional manufacturing.
Associated questions and answers:
How does rapid Prototyping contribute to sustainable product design and development?
Rapid prototyping aids in sustainable layout by decreasing fabric waste through specific production and enabling the testing of environmentally friendly materials.
In what methods can fast Prototyping be integrated into educational curriculums to enhance knowledge of engineering and layout?
Speedy Prototyping can offer hands-on experience, foster creativity, and provide immediate feedback in design and engineering education, bridging the space between theory and realistic utility.
How has fast Prototyping motivated the custom production of scientific devices and implants?
It has revolutionized custom clinical production by taking into account personalized solutions tailor-made to characterize patient anatomy, enhancing the fit and capability of clinical devices.
What function does fast prototyping play in the improvement of wearable tech?
It is pivotal in designing ergonomic and user-pleasant wearables, bearing in mind brief iterations and user testing to ensure comfort and capability.
How might technologies like AI and device learning enhance speedy prototyping techniques?
AI and gadget learning can optimize layout approaches, predict capacity design flaws, and automate factors of Prototyping, quickening up development and improving precision.
What effect might advances in product technology have on the future of rapid Prototyping?
Advances in product technology ought to increase the variety of elements and functionalities to be had in prototypes, from advanced durability to superior smart products that react to environmental adjustments.
Conclusion:
Prototyping, and mainly rapid prototyping, is not merely equipment for developing physical models; it is a catalyst for innovation and problem-fixing. These technologies democratize the design method, making for speedy iteration, experimentation, and creativity. They bridge the distance between abstract thoughts and tangible products, fostering a greater dynamic, efficient, and user-centred method of design and manufacturing. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to keep on revolutionizing how we deliver ideas to reality, allowing for the process to be easier to access, sustainable, and aligned with the ever-shifting desires and demands of our global economy. Contact TEAM Rapid for rapid prototyping services now!




