Embarking on a journey through the realm of manufacturing, we encounter the intricate process of injection molding. This method seamlessly integrates an array of injection molding materials, ranging from robust metals and delicate glasses to flexible elastomers and even delectable confections. Among these, the eminent protagonists are the ubiquitous thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. This dynamic duo in harmony with its co-stars, fashions an array of components, from intricate constituents to substantial automobile panels.

Table of Contents
- 1 The Versatility of Injection Molding Materials: Shaping Diversity
- 2 Unveiling the Allure of Acrylic (PMMA) in Injection Molding
- 3 Exploring the Appeal Injection Molding Materials: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- 4 A Symphony of Injection Molding Materials: Crafting Diversity
- 5 Conclusion of Injection Molding Materials
The Versatility of Injection Molding Materials: Shaping Diversity
Within the realm of manufacturing, injection molding emerges as a cornerstone process, seamlessly accommodating a broad spectrum of plastic materials. This adaptability has ingrained its creations into both domestic landscapes and industrial settings. Amid this array of possibilities, a selection of preeminent plastics takes center stage, each imbued with distinct attributes that contribute to the art of production.
Acrylic (PMMA) illuminates with its optical precision and durability, lending itself gracefully to applications ranging from lenses to outdoor signage. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) stands as a paragon of resilience and impact resistance, making it a favored choice for the fabrication of toys and automotive components. In contrast, Nylon Polyamide (PA) brings forth its robust mechanical strength and resistance to chemicals, aptly serving roles in gear mechanisms and bearings.
Stepping into prominence, Polycarbonate (PC) boasts an extraordinary balance of impact resistance and transparency, gracing the likes of eyeglass lenses and protective shields. The stage then hosts Polyoxymethylene (POM), renowned for its unyielding stiffness and dimensional stability, masterfully crafting intricate components like gears and bearings.
In the wings, Polypropylene (PP) takes its position, celebrated for its economical nature and chemical resistance, asserting its dominion over packaging and an array of consumer goods. Polystyrene (PS) makes its entrance, known for its structural rigidity and ease of processing, rendering it ideal for applications such as disposable tableware and food containers.
Amidst the ensemble, Polyethylene (PE) graces the scene, showcasing its remarkable flexibility and toughness, suiting roles that range from plastic bags to sturdy containers. The culmination of these materials within the craft of plastic molding yields an intricate tapestry of products, each tailored to fulfill the exacting needs of diverse applications. This symphony of materials embodies the essence of injection molding’s adaptability and its profound impact across industries and daily life.
Unveiling the Allure of Acrylic (PMMA) in Injection Molding
A Clear Canvas of Versatility
In the vibrant realm of injection molding, Acrylic emerges as a star player, renowned for its multifaceted charm. This polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) maestro captures attention with a blend of virtues that make it an embodiment of functional artistry.
Strength in Simplicity
Acrylic’s allure begins with a robust mechanical strength that belies its lightweight nature. Its transparent visage acts as a window to endless possibilities, inviting light to dance through its crystalline matrix. A testament to its durability, shatter resistance stands as a hallmark, making it a favored contender for scenarios where resilience meets elegance.
Crafting Brilliance, Post-Mold
The curtain rises on Acrylic’s encore act, wherein its brilliance truly shines. The ease with which it succumbs to machining post-injection molding grants it versatility appreciated by creators. This very attribute weaves a spell, transforming it into an ideal candidate for crafting lenses, signage, and captivating displays that adorn our world.
Notes of Caution
Yet, like any enigmatic protagonist, Acrylic bears its quirks. Its susceptibility to scratches and a penchant for accumulating oils and greases require a nuanced touch in handling and maintenance. This delicate interplay between durability and vulnerability adds a layer of intrigue to Acrylic’s narrative.
Exploring the Appeal Injection Molding Materials: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Enter the realm of injection molding, and one shall be met by the steadfast presence of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). Renowned for its exceptional attributes, ABS emerges as a stalwart player, boasting an array of qualities that make it a cornerstone of the craft.
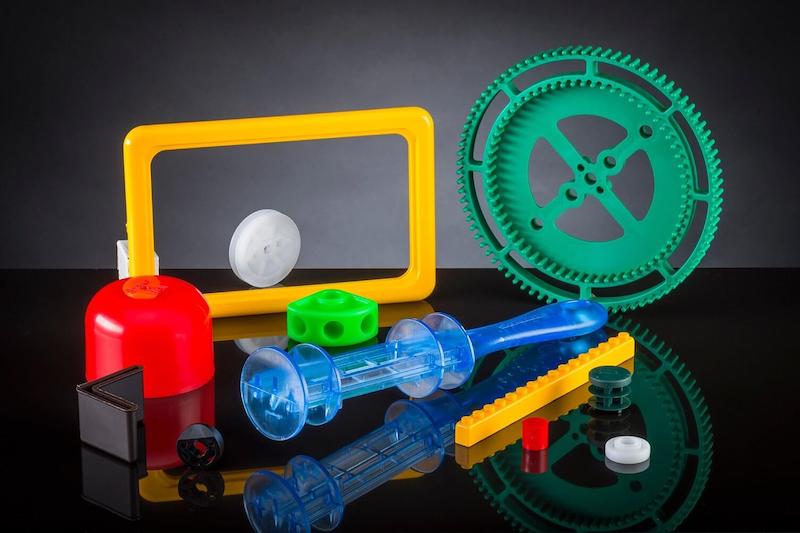

Strength and Beyond
Strength and toughness interlace in ABS’s DNA, crafting products that stand the test of time. Its inherent impact resistance ensures a shield against the rigors of everyday use, rendering it a formidable choice across various domains. But its prowess extends beyond mere robustness.
Resistance and Versatility
ABS dons a mantle of resistance, defying acids, bases, and oils with a confident demeanor. This chemical resilience imbues it with versatility that caters to diverse applications, from toys that withstand playful encounters to automotive parts that navigate demanding terrains.
Colors and Opacity
In the grand tapestry of ABS, a vibrant palette unfolds. Opaque by nature, ABS possesses the remarkable ability to embrace myriad hues through injection molding. This quality transforms it into a canvas of creativity, where it molds into forms that resonate with individual preferences.
Cautions in Sunlight and Moisture
Yet, amidst its splendor, a word of caution emerges. ABS’s resilience dwindles in the face of direct sunlight and damp environments. Here its vulnerabilities are laid bare, underscoring the need for mindful selection and application.
A Symphony of Injection Molding Materials: Crafting Diversity
Distinctive Properties
Nylon Polyamide (PA) strides forth with strength and chemical resilience, rendering it an apt choice for applications like gears and bearings. Polycarbonate (PC) assumes prominence with its formidable impact strength and transparent demeanor, making it ideal for eyeglass lenses and protective shields. The narrative advances with Polyoxymethylene (POM), characterized by high stiffness and impeccable dimensional stability, ensuring precision in intricate components.
Utility and Adaptability
Polypropylene (PP) emerges as a beacon of chemical resistance and economic viability, a material well-suited for packaging and consumer goods. Polystyrene (PS) showcases its structural rigidity and processing ease, making it a natural fit for disposable cups and food containers. Simultaneously, Polyethylene (PE) commands attention with its flexibility and robustness, embracing roles from plastic bags to resilient containers.
Versatility Redefined
Stepping into the spotlight, Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) and Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) encapsulate flexibility and intricate rubber injection molding potential. Their prowess in taking on complex shapes while maintaining a soft-touch quality positions them as key players in applications such as seals, gaskets, and ergonomic grips.
Conclusion of Injection Molding Materials
In the intricate landscape of rapid manufacturing, injection molding shines as a versatile artisan. Its canvas extends to a myriad of materials, each chosen with meticulous consideration for the intended product’s characteristics and specific application. This symbiotic dance of material selection underscores injection molding’s adaptability, unveiling a realm of endless potential.
Besides from injection molding, TEAM Rapid also offers 3d printing services, die casting, and CNC machining to meet your project needs. Contact our team today to request a free quote now!